Impact of cellular senescence on regenerative processes during aging Biology Diagrams Senescence was initially described for replicative cells and is still mainly linked to replication-competent cell moieties, whereas there is currently no clear association between the aging process and the turnover rate of cells in different tissues and organs [46,47], a fact that seemingly underlines the independence of the two processes.

Senescence can in turn drive the consequential aging hallmarks in response to damage: stem cell exhaustion and chronic inflammation. Other responses to damage, such as proteostatic dysfunction and nutrient signaling disruption, are also integrally linked with the senescence response.
Senescence and aging: Causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues Biology Diagrams
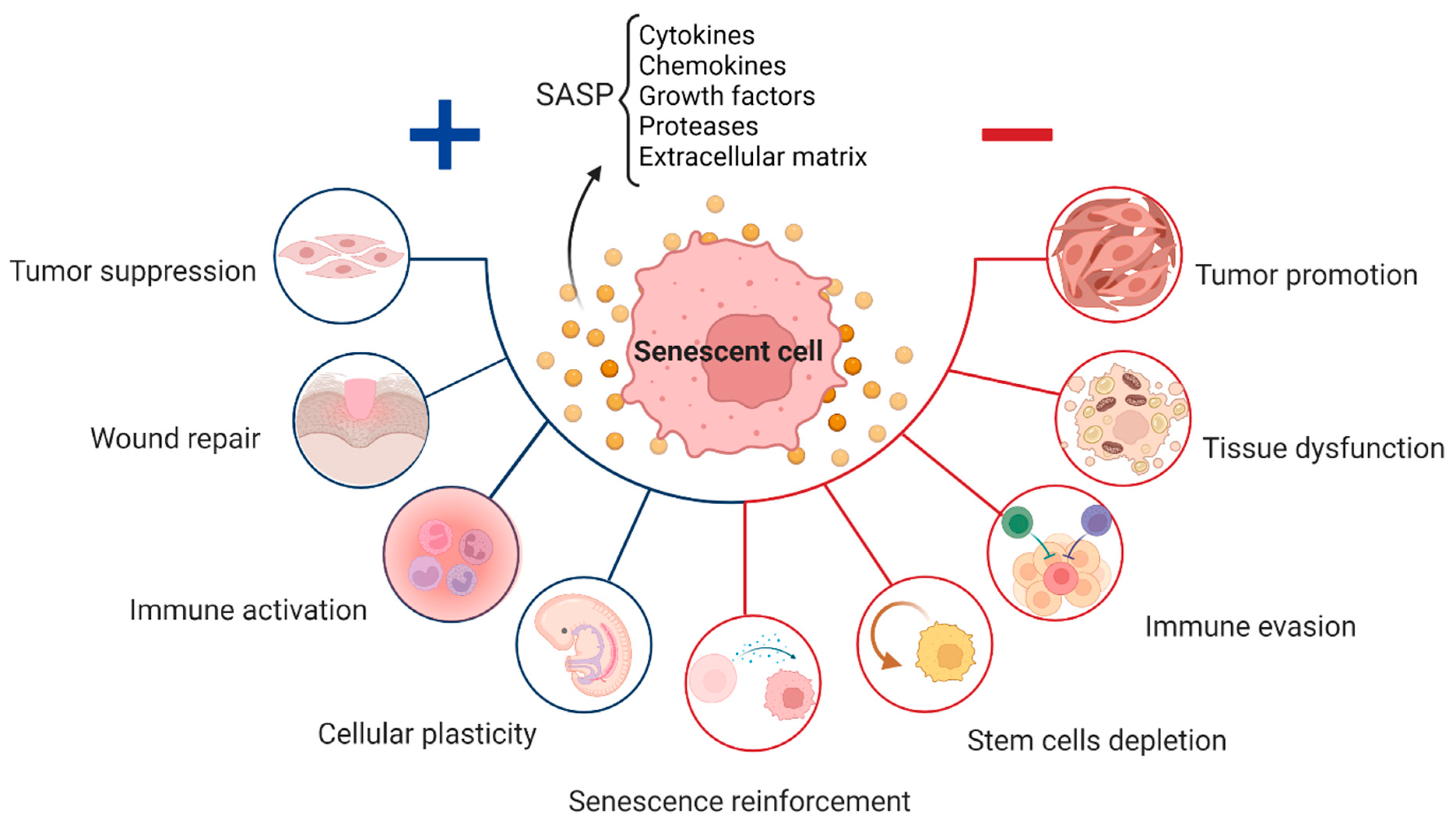
Cellular senescence is important for ensuring normal development and organism fitness against diseases including cancer. Meanwhile, accumulation of senescent cells during aging can be detrimental, contributing to age-related diseases. This review discusses recent advances in understanding the functional significance of senescence in these contexts and the potential translational impact.

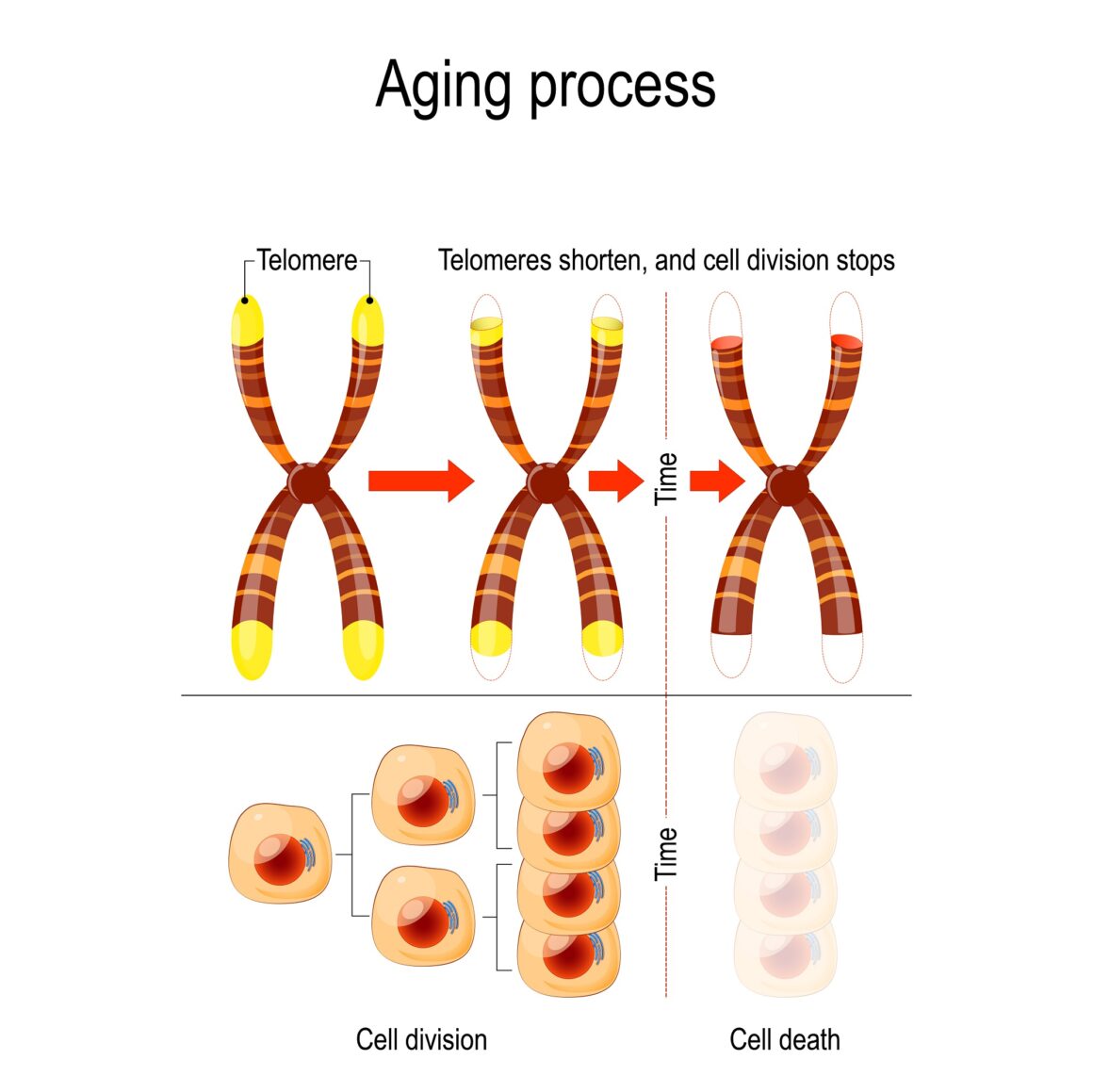
Senescence, from the Latin word senex, means "growing old," is an irreversible growth arrest which occurs in response to damaging stimuli, such as DNA damage, telomere shortening, telomere dysfunction and oncogenic stress leading to suppression of potentially dysfunctional, transformed, or aged cells. Cellular senescence is characterized by

Cellular Senescence in Health, Disease, and Lens Aging Biology Diagrams
Abstract. Background: Cellular senescence is a state of irreversible cell cycle arrest that serves as a critical regulator of tissue homeostasis, aging, and disease.While transient senescence contributes to development, wound healing, and tumor suppression, chronic senescence drives inflammation, tissue dysfunction, and age-related pathologies, including cataracts.